SLEEP APNEA
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that involves pauses in breathing during sleep—these are known as apneas or apnea events and can last for 10 seconds or more, occurring numerous times throughout the night. This can lead to fragmented sleep and reduced oxygen levels, having a profound impact on your well-being.
Left unaddressed, sleep apnea can result in excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty in maintaining concentration, and an elevated risk of accidents and cardiovascular complications. It is a serious condition that requires attention and care.
The most prevalent form of sleep apnea is Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), where the throat tissues block the upper airway despite ongoing efforts to breathe. Central Sleep Apnea, a less common form, arises when the brain fails to signal the muscles to breathe. Mixed Sleep Apnea combines elements of both obstructive and central sleep apnea.
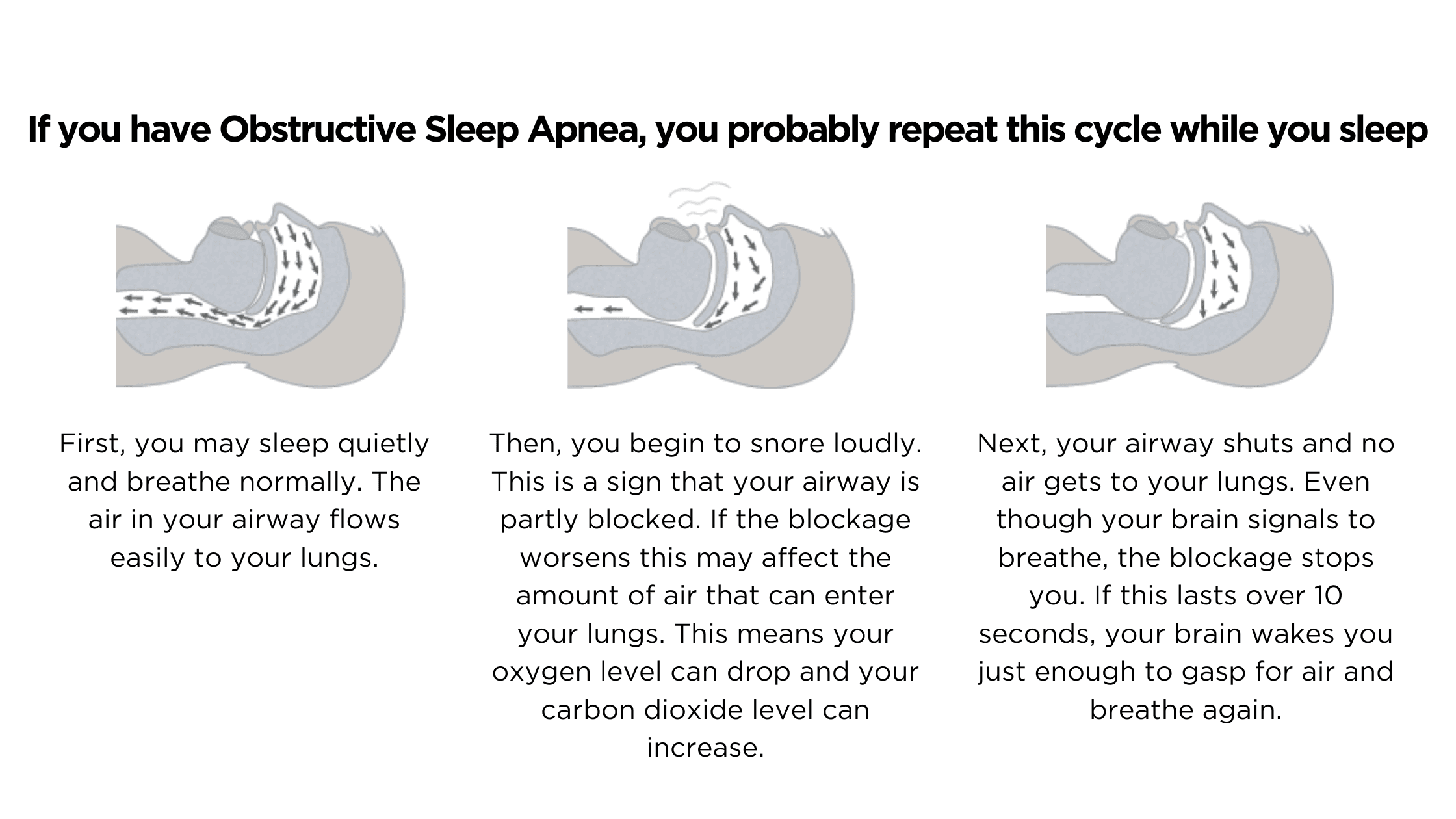
Often, individuals with sleep apnea are unaware of their condition as it develops gradually over time. Key indicators include unexplained daytime tiredness, loud snoring accompanied by breathing pauses, waking with a dry mouth or headache, irritability, and other symptoms that should not be overlooked.
Risk factors for sleep apnea include obesity, a larger neck circumference, being male, advanced age, a family history of the condition, smoking, and certain anatomical and medical conditions. The risks associated with untreated sleep apnea are considerable, potentially leading to hypertension, type II diabetes, heart attacks, strokes, and other serious health issues.
Download the "Sleep Apnea Handbook," a detailed guide designed to help you understand, manage, and seek treatment for sleep apnea. It's a step toward achieving the restorative sleep and optimal health you deserve.
For more information and support, please visit our friends at the Canadian Lung Association at www.lung.ca.

